最长回文子串
回文串就是原串和反转字符串相同的字符串。比如 aba,acca。前一个是奇数长度的回文串,后一个是偶数长度的回文串。
最长回文子串就是一个字符串的所有子串中,是回文串且长度最长的子串。
Brute Force 做法
枚举所有子串,判断是否是回文串,然后寻找最大长度。寻找所有子串要两重循环,判断是否是回文要一重循环,总体时间复杂度 $O(n^3)$。
稍微优化一下,可以枚举对称中心,然后向两边扩展,直到遇到两个不同的字符,枚举下一个对称中心,寻找其中的最大长度,时间复杂度 $O(n^2)$。
还可以使用 DP 解决,求原串与反转字符串的最长公共子序列 (LCS),时间复杂度 $O(n^2)$。
Manacher 算法
接下来就是重点了,Manacher 算法,在1975年由一个叫 Manacher 的人发明的。能够在 $O(n)$ 的时间求得最长回文子串。
前面提到,回文串有奇数长度的和偶数长度的,分类讨论有些复杂,可以参考这里。为了避免分类讨论,可以使用一个技巧:在字符串首尾以及每两个字符之间插入一个 '#'。比如 abaacca,转换后就是 #a#b#a#a#c#c#a#。那么不管是奇回文 aba 还是偶回文 acca,转换后都是奇回文 (#a#b#a# 和 #a#c#c#a#)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| string init(string s) {
string res;
res += '@';
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
res += '#';
res += s[i];
}
res += '#';
res += '$';
return res;
}
|
Manacher 算法的思想来自于上述枚举对称中心的思想。该算法需要维护一个 $len$ 数组,$len[i]$ 代表 $i$ 为中心的最长回文子串的长度。
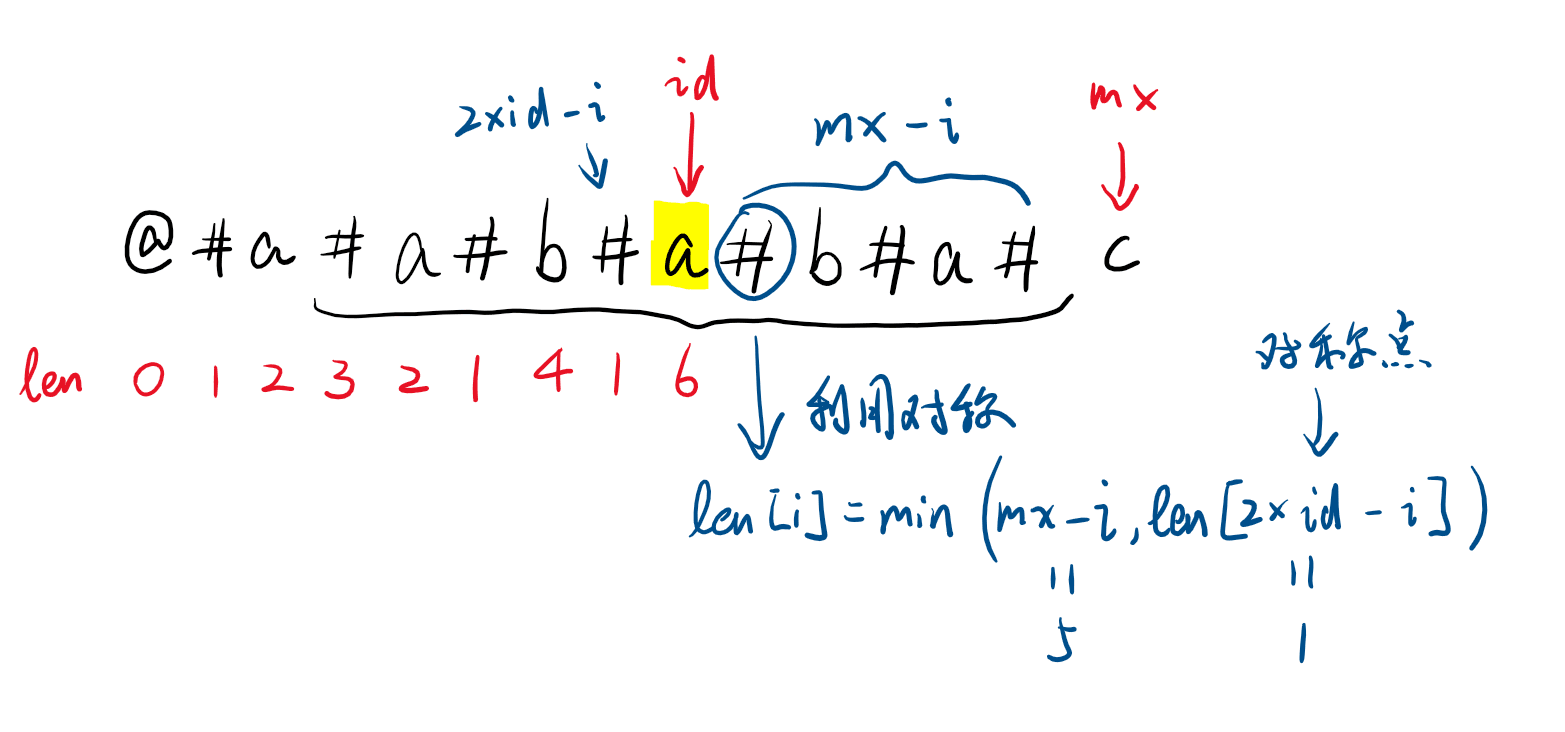
设 $s$ 为原字符串,$mx$ 为之前计算的回文串中右端点的最大值,这个回文串的中心位置为 $id$,也就是 $mx = id + len[id]$。
每次计算的时候,$id$ 的右边和左边是对称的,因此计算右边的时候不需要用从对称中心向两边扩展的思想,而是只用一行代码解决:len[i] = min(mx - i, len[2 * id - i]);,这也是 Manacher 中最关键的一行代码。
如下图所示,$id$ 右边到 $mx$ 之间的子串与 $id$ 左边是对称的,所以右边的 $len[i]$ 最大长度为左边与之对称的 $len[2\times id - i]$,由于右边的回文串不能超过 $mx$ (原因见第 2 张图),所以 len[i] = min(mx - i, len[2 * id - i]);。
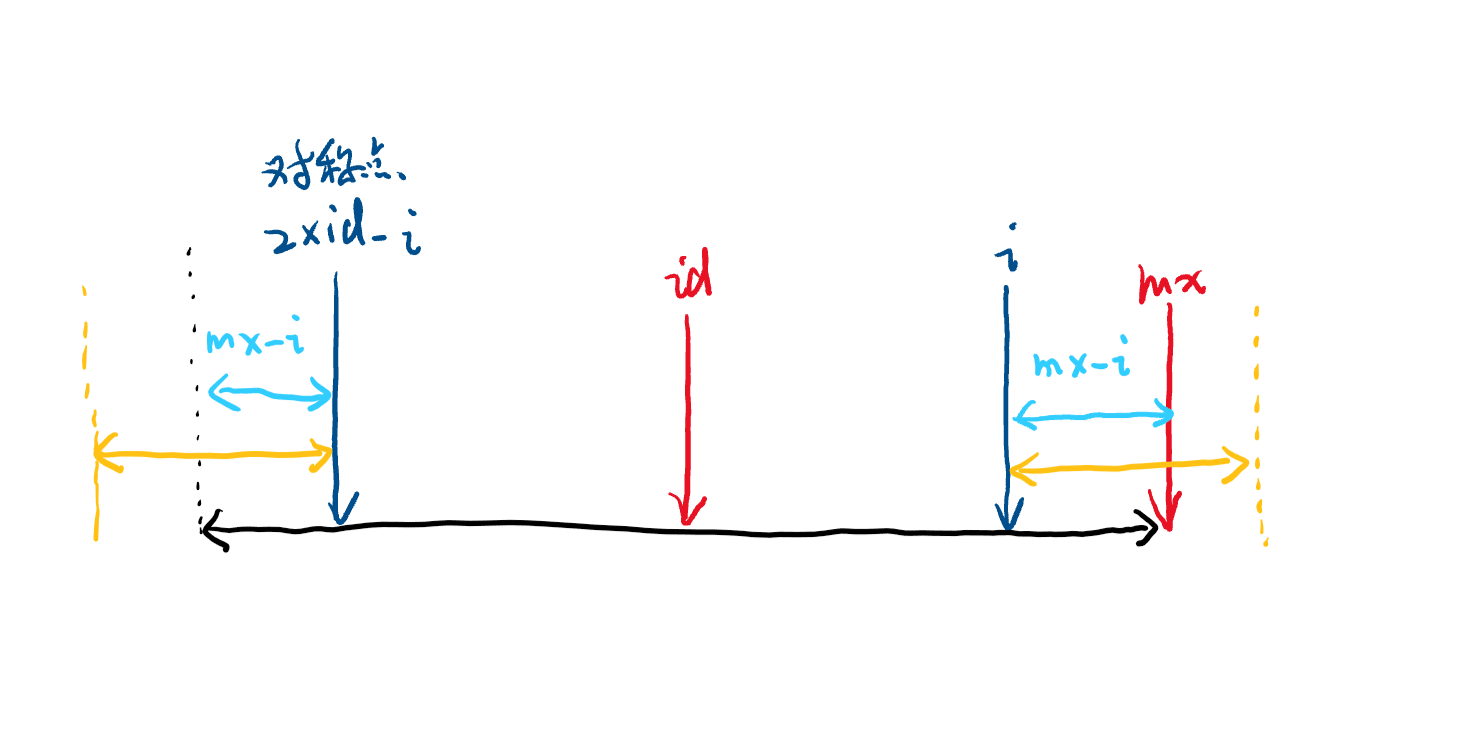
$id$ 右边的回文串长度不能超过 $mx - i$ 的原因是,如果 $len[2 * id - i]$ 更长,如下图的黄色部分,那么右边的黄色部分与左边的黄色部分相同,那么黑色部分应该可以更长,产生矛盾。
理解了上面的内容基本上就理解了 Manacher 算法了。
代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| int Manacher(string s) {
memset(len, 0, sizeof(len));
int mx = 0, id = 0;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < s.size() - 1; ++i) {
if(mx > i) {
len[i] = min(mx - i, len[2 * id - i]);
} else {
len[i] = 1;
}
while(s[i - len[i]] == s[i + len[i]]) {
++len[i];
}
if(i + len[i] > mx) {
mx = i + len[i];
id = i;
}
ans = max(ans, len[i]);
}
return ans - 1;
}
|
模板题:HDU 3068 最长回文
题目链接:HDU 3068 最长回文
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 220000;
string init(string s) {
string res;
res += '@';
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
res += '#';
res += s[i];
}
res += '#';
res += '$';
return res;
}
int len[maxn];
int Manacher(string s) {
memset(len, 0, sizeof(len));
int mx = 0, id = 0;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < s.size() - 1; ++i) {
if(mx > i) {
len[i] = min(mx - i, len[2 * id - i]);
} else {
len[i] = 1;
}
while(s[i - len[i]] == s[i + len[i]]) {
++len[i];
}
if(i + len[i] > mx) {
mx = i + len[i];
id = i;
}
ans = max(ans, len[i]);
}
return ans - 1;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
string s;
while (cin >> s) {
string tmp = init(s);
cout << Manacher(tmp) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
参考
Manacher算法图解
Manacher算法

