题目链接:1127. 多边形面积(计算几何)
题意
按逆时针顺序给出 $n$ 个点的坐标,求这些点围成的多边形的面积。
思路
选择多边形上的一个点,然后每次枚举之后的两个点,计算叉积,注意要保留符号,对所有的叉积的结果相加就是多边形的面积。
举个栗子:
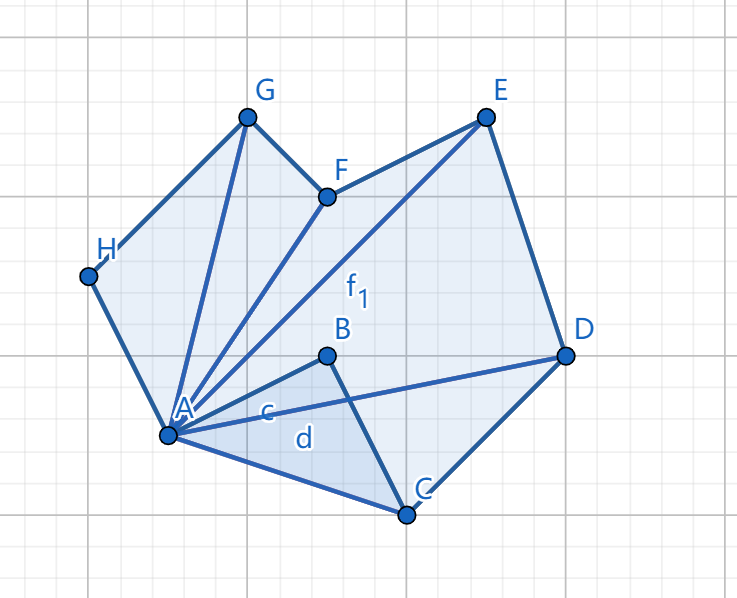
计算上图多边形 $ABCDEFGH$ 的面积,选择 $A$ 点,则面积等于 $\frac{1}{2} (\boldsymbol {AB \times AC} + \boldsymbol {AC \times AD} + \boldsymbol {AD \times AE} + \boldsymbol {AE \times AF} + \boldsymbol {AF \times AG} + \boldsymbol {AG \times AH})$。其中 $\triangle ABC$ 的面积是负的,而 $\triangle ACD$ 与 $\triangle ADE$ 的面积都是正的,则多边形 $ABCDE$ 的面积相当于多边形 $ACDE$ 的面积减去 $\triangle ABC$ 的面积。
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
| #include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
const db eps = 1e-10;
const db pi = acos(-1.0);
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const ll maxn = 100 + 10;
inline int dcmp(db x) {
if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
return x > 0? 1: -1;
}
class Point {
public:
double x, y;
Point(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
void input() {
scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y);
}
bool operator<(const Point &a) const {
return (!dcmp(x - a.x))? dcmp(y - a.y) < 0: x < a.x;
}
bool operator==(const Point &a) const {
return dcmp(x - a.x) == 0 && dcmp(y - a.y) == 0;
}
db dis2(const Point a) {
return pow(x - a.x, 2) + pow(y - a.y, 2);
}
db dis(const Point a) {
return sqrt(dis2(a));
}
db dis2() {
return x * x + y * y;
}
db dis() {
return sqrt(dis2());
}
Point operator+(const Point a) {
return Point(x + a.x, y + a.y);
}
Point operator-(const Point a) {
return Point(x - a.x, y - a.y);
}
Point operator*(double p) {
return Point(x * p, y * p);
}
Point operator/(double p) {
return Point(x / p, y / p);
}
db dot(const Point a) {
return x * a.x + y * a.y;
}
db cross(const Point a) {
return x * a.y - y * a.x;
}
};
Point p[maxn];
int n;
db area() {
if(n < 3) return 0.0;
db ans = 0.0;
for(int i = 2; i < n; ++i) {
ans += (p[i] - p[1]).cross(p[i + 1] - p[1]);
}
return ans * 0.5;
}
int main() {
while(~scanf("%d", &n) && n) {
db s = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
p[i].input();
}
s = area();
printf("%.1lf\n", fabs(s));
}
return 0;
}
|
